Walter Russell Periodic Table: A New Perspective on Elements
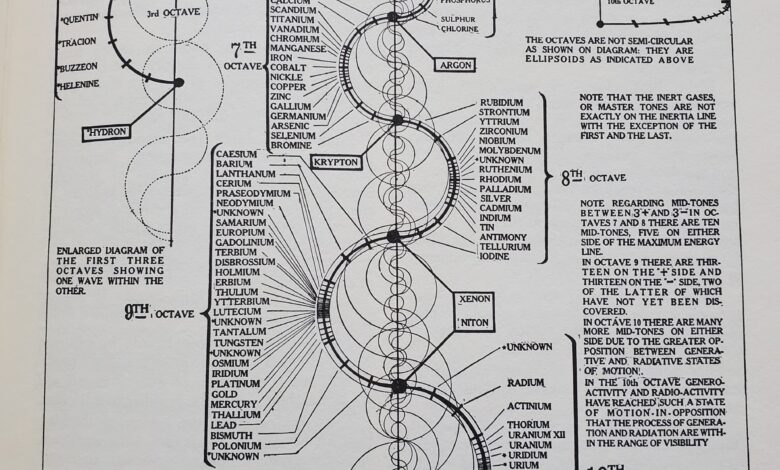
The Walter Russell periodic table offers a unique way of understanding elements, energy, and the universe. Unlike the traditional periodic table used in chemistry, Walter Russell’s version presents a dynamic, spiral-based arrangement that aligns with cosmic energy flow. This groundbreaking concept challenges conventional science and provides an alternative view of matter and its transformation.
Who Was Walter Russell?
Walter Russell (1871–1963) was a polymath, meaning he excelled in multiple fields, including painting, sculpture, philosophy, and science. His theories on the structure of the universe and the nature of elements differed from mainstream science, emphasizing energy, consciousness, and the rhythmic cycles of nature. He believed everything in the universe was part of a divine order, guided by principles of balance and harmony.
The Unique Concept of the Walter Russell Periodic Table
The Walter Russell periodic table is not just a chart of elements; it represents the wave cycles of energy that create and sustain matter. Unlike the traditional periodic table, which organizes elements based on atomic number and electron configuration, Russell’s version is based on the idea that elements evolve and transform in a continuous wave cycle.
Key Features of the Walter Russell Periodic Table
- Spiral Design – Instead of a rectangular format, Russell’s table follows a spiral shape, indicating the motion and transformation of elements.
- Energy-Based Approach – It suggests that elements emerge from waves of energy and are part of a continuous cycle.
- Octaves of Elements – Russell grouped elements into octaves, much like musical notes, signifying their vibrational nature.
- Predictive Power – His model suggested the existence of undiscovered elements and predicted changes in known elements.
How the Walter Russell Periodic Table Differs from the Traditional Periodic Table
The traditional periodic table, created by Dmitri Mendeleev, categorizes elements based on their atomic structure and properties. Walter Russell, however, introduced a more dynamic perspective. Below is a comparison of both models:
| Feature | Traditional Periodic Table | Walter Russell Periodic Table |
| Structure | Tabular, organized by atomic number | Spiral, wave-based arrangement |
| Focus | Atomic structure and chemical properties | Energy transformation and cycles |
| Element Grouping | Periods and groups | Octaves (like musical scales) |
| Changeability | Fixed categories | Elements evolve and change over time |
| Scientific Basis | Empirical observations | Philosophical and energetic concepts |
The Concept of Element Octaves
One of the most fascinating ideas in the Walter Russell periodic table is the use of octaves. He believed that elements were arranged in a sequence similar to musical notes, where each octave represented a complete cycle of elemental transformation. Just as sound waves follow a frequency pattern, elements follow an energetic rhythm.
Understanding Octaves in Elements
- Each octave contains a set of elements that evolve from one another.
- Elements within an octave share energetic similarities, just as musical notes in the same octave harmonize.
- Higher octaves represent more advanced states of matter.
- Light and energy play a major role in the transformation of elements.
The Role of Light and Energy in the Walter Russell Periodic Table
Walter Russell emphasized the importance of light and energy in the formation of matter. He argued that all elements are formed through waves of light, which condense into different atomic structures over time. Unlike traditional chemistry, which views atoms as stable units, Russell suggested that atoms continuously cycle through energy waves.
Light as the Source of Matter
- Matter is a form of compressed light energy.
- Energy waves move in spirals, influencing the transformation of elements.
- Elements are created and destroyed as they move through cycles of energy.
- Atoms are not fixed but evolve based on the surrounding energy fields.
Implications of the Walter Russell Periodic Table
If Walter Russell’s model is correct, it could transform our understanding of chemistry, physics, and even biology. His ideas suggest that matter is not static but constantly evolving through energy cycles.
Potential Scientific and Technological Applications
- New Element Discovery – Russell’s table predicts elements that may not yet be recognized by modern science.
- Alternative Energy Sources – Understanding energy cycles could lead to new ways of harnessing power.
- Biological Implications – If matter evolves through energy waves, it could change how we understand life and genetics.
- Cosmology and Space Exploration – A wave-based element system could provide insights into how matter forms in space.
Challenges and Criticism
Despite its fascinating ideas, the Walter Russell periodic table is not widely accepted in mainstream science. Critics argue that:
- It lacks empirical data to support its claims.
- The traditional periodic table has proven highly accurate in chemical reactions.
- Russell’s model is more philosophical than scientific.
- His predictions require more experimental validation.
However, many researchers and alternative scientists find Russell’s ideas compelling and continue to explore their potential.
The Legacy of Walter Russell
Walter Russell’s work extends beyond the periodic table. His theories on universal energy, consciousness, and artistic expression have inspired many. Even though his periodic table is not fully recognized by mainstream science, it has encouraged new ways of thinking about matter, energy, and the universe.
Why His Ideas Still Matter
- Encourages scientific curiosity and open-minded exploration.
- Bridges science, philosophy, and spirituality.
- Inspires alternative approaches to energy and technology.
- Challenges traditional views, pushing science to evolve.
Conclusion
The Walter Russell periodic table presents an extraordinary vision of the elements, focusing on energy cycles, octaves, and the role of light in matter’s transformation. While not widely accepted, it challenges traditional science to think beyond rigid structures and explore the dynamic nature of the universe. Whether viewed as science, philosophy, or art, Russell’s periodic table remains a fascinating contribution to our understanding of existence.




